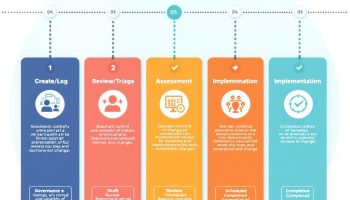
The 5 Phases of Project Management
The 5 phases of project management PMBOK provide a structured framework for successful project delivery, beginning with project initiation, a critical phase that sets the foundation for all subsequent work. By establishing clear business needs, defining project objectives, and securing executive sponsorship, you create a strategic roadmap that guides the entire project lifecycle through planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and ultimately closing.
Key Takeaways:
- Project initiation formally authorizes a project and defines its core purpose, objectives, and success criteria
- The Project Charter is the essential document that captures high-level requirements and establishes project governance
- Strategic alignment with organizational goals is crucial during the initiation phase
- Executive sponsorship and stakeholder identification are fundamental to project success
- The initiation phase serves as a critical go/no-go decision point to prevent resource waste on poorly conceived initiatives
Project initiation marks the official start of your project journey. During this phase, you’ll identify business requirements, establish key objectives, and secure the necessary approvals to proceed. This foundation ensures your project addresses actual business needs while setting realistic expectations for all involved parties.
Creating a comprehensive Project Charter stands as your first major milestone. This document outlines the project’s purpose, high-level scope, and preliminary budget estimates. The charter also identifies key stakeholders and establishes governance structures that will guide decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Strategic alignment must remain at the forefront during initiation. Your project should directly support organizational goals and contribute to business value. This connection helps justify resource allocation and builds support across organizational levels.
Executive sponsorship proves essential for project success. Your sponsor provides authority, resources, and removes obstacles that might impede progress. Identifying this individual early and securing their active commitment improves your project’s chances for success.
The initiation phase concludes with a formal decision point. This evaluation determines if the project should advance to planning or be reconsidered. Making informed decisions at this stage prevents wasting resources on initiatives that don’t align with organizational priorities or lack feasible implementation paths.
Stakeholder identification forms another crucial element of project initiation. You’ll need to document everyone affected by or influencing the project outcomes. Understanding these individuals’ expectations, influence levels, and communication needs helps manage stakeholder relationships effectively from day one.
Risk assessment begins during initiation with preliminary identification of major uncertainties that could impact project success. While detailed risk planning happens later, early awareness of significant threats or opportunities shapes your initial approach and resource planning.
Budget considerations start taking shape during initiation. You’ll develop high-level cost estimates that inform funding decisions. These preliminary figures help establish financial boundaries and set expectations with sponsors and stakeholders about resource requirements.
Project scope definition begins during initiation but remains at a high level. You’ll outline what the project will and won’t deliver, establishing boundaries that guide detailed planning in the next phase. Clear scope definition helps prevent scope creep as the project progresses.
The initiation phase creates the foundation for project success. Taking time to properly authorize the project, define its purpose, secure sponsorship, and align with organizational goals positions you for effective execution in subsequent phases. This careful groundwork maximizes the likelihood of delivering value through your project initiatives.
“Project initiation is the cornerstone of successful project management, where clear objectives and strategic alignment lay the groundwork for effective execution. By securing executive sponsorship and defining success criteria, project managers can transform ideas into actionable roadmaps, steering projects toward impactful delivery.”
Project Initiation: Establishing the Foundation
Project initiation marks the first of the 5 phases of project management PMBOK and sets the stage for everything that follows. This critical phase formally authorizes your project while clearly defining business needs and expected outcomes.
The cornerstone deliverable during initiation is the Project Charter—a document that captures high-level requirements, objectives, success criteria, and preliminary budget estimates. Your charter also establishes the project manager’s authority and identifies key stakeholders who’ll influence your project’s success. Without this foundation, projects often drift without clear purpose or support.
This phase serves as a crucial go/no-go decision point, preventing unauthorized projects from consuming valuable resources. You’ll need to ensure strategic alignment with organizational goals and secure executive sponsorship to move forward.
Key Components of Successful Initiation
When launching a project, you should focus on these essential elements:
- Defining the business case and project justification
- Identifying measurable objectives and success criteria
- Documenting high-level scope boundaries and exclusions
- Recognizing major stakeholders and their expectations
- Assigning a project manager with appropriate authority
- Securing formal approval to proceed
Project initiation isn’t just administrative—it establishes why your project exists. As noted in stakeholder identification best practices, identifying and aligning key players during this phase prevents major roadblocks later.
Tools like Microsoft 365 and Teams can support your initiation activities, facilitating collaboration among stakeholders. When done properly, this phase answers fundamental questions about purpose, scope, and governance that will guide all subsequent work.
Effective project initiation requires balancing thoroughness with speed. You need enough detail to proceed confidently but shouldn’t get bogged down in excessive planning. Remember that your go/no-go decision represents an important checkpoint that prevents resource waste on poorly conceived initiatives.
The 5 phases of project management PMBOK framework begins here with initiation, setting the tone for your entire project. By investing adequate time and attention in this foundation phase, you’ll position your project for success across subsequent planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closing phases.
Expert Insight: To establish a solid foundation during project initiation, prioritize the creation of a clear and comprehensive Project Charter that outlines the business case, objectives, success criteria, and stakeholder expectations. Engage key stakeholders and secure executive sponsorship early to align the project with organizational goals and prevent resource misallocation. Remember, this phase is pivotal for defining purpose and governance, setting the tone for all subsequent project phases.
Comprehensive Project Planning
Project planning forms the backbone of successful project management and requires meticulous attention to detail. In the PMBOK framework, this second phase is where you’ll develop an integrated Project Management Plan that details how you’ll achieve your project objectives. Planning is iterative rather than linear—you’ll likely revisit your plans as new information emerges throughout the project lifecycle.
During this phase, you’ll create several subsidiary plans focusing on the 5 phases of project management PMBOK recommends. These include:
- Scope definition through a detailed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Schedule development using Gantt charts or similar tools
- Budget allocation and resource planning
- Quality standards and management approaches
- Risk identification, analysis and response planning
- Communications strategy and stakeholder engagement plans
You’ll also need to define team roles and establish change control protocols that will guide how modifications are managed throughout the project. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK outlines require this planning phase to be thorough and comprehensive.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Planning
Leveraging the right tools can significantly enhance your planning efforts. Software solutions like Microsoft Project, Asana, and Jira provide powerful capabilities for project planning workflow management. These tools help you visualize dependencies, allocate resources efficiently, and track progress against your baseline plan.
Remember that sponsor approval of your complete project management plan is crucial before moving to execution. Without this formal sign-off, you risk proceeding without proper authorization or alignment. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK framework emphasizes this approval as a critical milestone marking the transition from planning to execution.
Effective planning requires balancing detail with flexibility. Your plans should be specific enough to provide clear direction but adaptable enough to accommodate the inevitable changes that will emerge. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK approach recognizes this balance, encouraging you to develop comprehensive plans while maintaining room for scope adjustments when necessary.

Execution and Resource Mobilization
The execution phase represents the heart of your project lifecycle where the 5 phases of project management PMBOK principles come alive through action. This phase consumes the largest portion of your project budget and schedule as your team produces deliverables according to the established plan.
During execution, you’ll coordinate team activities, manage resources, and implement the project management plan. Your role shifts from planning to active leadership as you guide your team through implementation challenges. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK framework emphasizes that success during execution requires consistent project collaboration and clear direction.
Key activities during this phase include:
- Implementing quality assurance processes
- Conducting regular status meetings
- Managing team performance and conflicts
- Executing procurement activities
- Distributing information to stakeholders
Resource allocation becomes particularly crucial as this phase typically requires 60-80% of total project resources. You’ll need to manage competing priorities and ensure the right skills are available at the right time. Effective capacity planning helps prevent bottlenecks that can derail progress.
Common challenges during execution include scope creep, resource conflicts, and unexpected risks. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK methodology recommends establishing clear change control procedures to manage these issues effectively. When problems arise, your ability to make timely decisions while maintaining team morale becomes essential.
Execution Tools and Techniques
The PMBOK Guide identifies several tools to support execution effectiveness:
- Team management systems for tracking assignments and progress
- Information management systems for documentation and collaboration
- Work authorization systems to control task initiation
- Status review meetings to maintain alignment
- Issue logs to track and resolve problems
Your execution phase will benefit from project communication techniques that keep stakeholders informed without overwhelming them with details. The 5 phases of project management PMBOK approach emphasizes that execution success depends on both technical competence and interpersonal skills.
Remember that while execution focuses on producing deliverables, it must remain aligned with the broader project objectives. Regular checkpoints with sponsors help ensure the work maintains strategic relevance throughout this intensive phase.
Expert Insight: In the execution phase of project management, effective resource mobilization is critical, as this stage consumes the majority of your budget and schedule. Prioritize clear communication and regular status checks to mitigate risks like scope creep and resource conflicts, ensuring your team stays aligned with project objectives. By balancing technical competencies with strong leadership, you can navigate challenges and maintain engagement throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Monitoring and Controlling for Project Success
Monitoring and controlling is one of the crucial 5 phases of project management PMBOK that runs parallel to the execution phase rather than following it sequentially. You’ll find this phase particularly valuable as it creates a continuous feedback loop allowing for timely adjustments and corrections throughout your project lifecycle.
During this phase, you’ll track actual performance against your baseline project plan using powerful metrics like Earned Value Management (EVM). This methodology helps you answer two essential questions: “Are we on schedule?” and “Are we within budget?” by calculating the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) and Cost Performance Index (CPI). When these indices fall below 1.0, you’ll need to take corrective action to bring the project back on track.
Integrated change control represents another cornerstone of this phase. You’ll establish formal processes for reviewing, approving, and implementing changes while maintaining scope integrity. This helps prevent the common issue of scope creep that can derail even well-planned projects.
Key Components of Monitoring and Controlling
The monitoring and controlling phase encompasses several vital activities that help keep your project on target:
- Performance measurement against established baselines (scope, schedule, cost, quality)
- Variance analysis to identify deviations from the plan
- Regular stakeholder reporting through dashboards and status meetings
- Risk monitoring to identify new threats and opportunities
- Quality control through inspections and testing
- Issue management and resolution tracking
Effective monitoring requires robust project management software that centralizes data and provides real-time visibility. Tools like Microsoft Project, Jira, and Monday.com offer integrated dashboards that display key performance indicators and highlight areas needing attention.
You’ll also conduct regular plan vs. actual comparisons during this phase. These reviews allow you to implement corrective actions before minor issues escalate into major problems, ultimately increasing your chances of delivering within the approved constraints.
By mastering the monitoring and controlling phase of the 5 phases of project management PMBOK, you’ll develop greater predictability in your projects and build confidence among stakeholders through transparent performance reporting and proactive management.
Projects with effective monitoring and controlling have a 25% higher success rate than those that lack these practices.
hbr.org