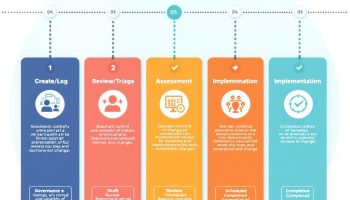
The Agile Steps in Project Management
The agile steps transform project management by starting with concept development and moving through iterative planning and execution cycles. Teams can deliver value quickly, adapt to changing needs, and maintain a flexible workflow by dividing projects into short, focused sprints that prioritize improvement and client satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Agile methodologies focus on iterative development with short (1-4 week) sprints that deliver functional features.
- Cross-functional teamwork and ongoing feedback form the core of the agile approach.
- Feature prioritization and continuous quality testing are vital for successful agile implementation.
- Adaptability sets agile apart from conventional project management techniques.
- Regular sprint evaluations enable teams to refine their processes consistently.
The Scrum framework provides a structured implementation of these agile principles. The Agile Manifesto outlines the foundational values that guide this methodology. For organizations seeking certification, the Scrum Alliance offers resources to formalize your agile knowledge.
“Embracing agile methodologies transforms project management by fostering a culture of iterative development, where short sprints deliver consistent value and adaptability reigns supreme. This dynamic approach not only prioritizes collaboration and continuous feedback but also empowers teams to evolve rapidly, ensuring stakeholder satisfaction at every turn.”
The Agile Lifecycle: Key Iterative Steps
Agile steps explained properly can transform how you manage projects. The agile lifecycle follows a series of iterative steps that build upon each other to deliver value incrementally. You’ll find this approach particularly effective when requirements change frequently or when you need to adapt quickly to market demands.
The agile lifecycle begins with ideation and concept development. During this phase, you’ll define the project vision and initial scope while collaborating with stakeholders to gather requirements. Prioritizing project objectives is crucial here – it helps you focus on delivering the most valuable features first. Effective stakeholder management during ideation sets the foundation for project success.
Strategic planning follows with the creation of a product roadmap and initial backlog. You’ll assemble your team and plan resources while progressively elaborating project details. This isn’t about creating detailed plans for the entire project but rather establishing just enough structure to begin work. The agile steps explained here differ significantly from traditional approaches as they embrace change rather than resist it.
Execution Through Iterative Cycles
The core of agile steps explained is found in the execution phase. You’ll organize work into short timeboxed cycles (sprints) typically lasting 1-4 weeks. These sprints feature:
- Daily stand-up meetings to synchronize activities
- Cross-functional collaboration throughout development
- Incremental product development with working deliverables
- Continuous integration and design refinement
- Sprint reviews to demonstrate completed work
Project collaboration techniques are essential when implementing these agile steps explained in practice. Your team will work closely together, breaking down silos that often slow traditional projects.
Continuous testing and quality assurance run parallel to development activities. You’ll implement real-time quality validation with rapid feedback loops that enable immediate bug detection and resolution. This approach ensures that quality is built into the product rather than tested afterward.
| Aspect | Agile Steps | Traditional Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Progressive and adaptive | Comprehensive upfront |
| Development | Iterative with frequent delivery | Sequential phases |
| Testing | Continuous throughout | Often at project end |
| Changes | Expected and welcomed | Avoided or strictly controlled |
| Customer involvement | Regular throughout | Limited, often at beginning and end |
By following these agile steps explained methodically, you’ll create a rhythm of continuous improvement. Agile implementation guides can provide additional context for applying these principles effectively in your organization.
Expert Insight: Understanding and implementing the Agile lifecycle is essential for adapting to dynamic project demands and enhancing overall productivity. Focus on maintaining open communication and collaboration with stakeholders during the ideation phase to establish a robust project foundation. Embrace iterative cycles during execution, allowing for continuous feedback and quality assurance to ensure your team delivers valuable, high-quality outcomes efficiently.
Ideation and Concept Development
The foundation of any successful agile project begins with solid ideation and concept development. This critical first step in the agile steps explained framework helps you define your project’s vision while maintaining flexibility for future iterations. You’ll need to establish clear objectives without getting locked into rigid specifications that could hinder adaptability later.
During this phase, you’ll collaborate with stakeholders to gather requirements and create a shared understanding of the project’s purpose. Effective active listening becomes essential when collecting diverse perspectives that will inform your project direction. This collaborative approach ensures your agile steps explained process starts with a comprehensive view of needs and expectations.
Prioritizing Project Objectives
Once you’ve gathered initial requirements, prioritization becomes crucial. You’ll need to:
- Sort features based on business value and customer needs
- Identify minimum viable product (MVP) components
- Establish clear acceptance criteria for each objective
- Determine which agile steps explained elements need immediate attention
- Create preliminary user stories that capture core functionality
This prioritization ensures you’ll focus development efforts on the most valuable elements first. Many projects fail when teams don’t establish these priorities early, leading to wasted resources on less important features.
A well-executed ideation phase sets the stage for strategic planning and resource allocation. By developing a clear concept with prioritized objectives, you’ve created a solid foundation while maintaining the flexibility that makes agile steps explained methodologies so effective.
The agile steps explained approach differs significantly from traditional methodologies in this phase. Rather than attempting to define all requirements upfront, you’ll embrace the concept of progressive elaboration. This means acknowledging that requirements will evolve throughout the project lifecycle and creating space for that evolution.
Your concept development should balance clarity with adaptability. Too much detail too early contradicts agile principles, while too little direction creates confusion. Finding this balance requires experience with agile steps explained processes and strong project communication skills.
Remember that agile steps explained methodologies thrive on collaboration. Involve developers, designers, and business stakeholders during ideation to ensure technical feasibility aligns with business objectives. This cross-functional input helps identify potential challenges early when they’re easier and less expensive to address.
Companies that excel in design and collaboration during the ideation phase are 75% more likely to deliver successful projects on time and within budget.
forbes.com
Strategic Planning and Resource Allocation
Effective strategic planning is the backbone of your agile steps explained approach. It’s where your project takes shape with flexibility built right in. You’ll need to create a product roadmap that outlines high-level features and milestone deliverables while allowing for refinement throughout the development process.
Your product backlog serves as the central repository for all work items that need to be completed. Unlike traditional project plans, agile backlogs are dynamic, living documents that evolve as you learn more about customer needs and market conditions. Strategic planning in agile requires continuous prioritization based on business value and technical dependencies.
Resource allocation in agile differs significantly from traditional approaches. Instead of detailed upfront planning, you’ll implement progressive elaboration – planning in just enough detail for the immediate future while maintaining a broader vision for later stages. This approach optimizes your team’s flexibility to respond to changing requirements.
Essential Agile Planning Elements
When implementing agile steps explained methodology, include these key components in your planning process:
- User Stories: Break down requirements into manageable chunks from the user’s perspective
- Story Points: Estimate relative effort rather than exact hours to accommodate uncertainty
- Velocity Tracking: Measure team capacity based on previous sprint performance
- Release Planning: Group related user stories into potential release candidates
- Sprint Planning: Detail only what can be accomplished in the next 1-4 week iteration
Your resource allocation strategy should emphasize cross-functional team composition rather than siloed specialization. Mastering strategic planning in agile means focusing on team capacity and capabilities instead of individual resource utilization percentages.
Effective backlog refinement sessions serve as the bridge between strategic vision and tactical execution. During these sessions, you’ll analyze and break down complex work items, ensuring your team can deliver incremental value in each sprint while maintaining alignment with the overall product direction.
Agile steps explained planning also incorporates built-in adaptation points. Rather than viewing changes as disruptions, you’ll establish regular inspection cadences to validate assumptions and adjust course accordingly. This ensures your resource investments remain aligned with evolving business priorities and customer feedback throughout the development lifecycle.
Companies that prioritize strategic planning and resource allocation are 12 times more likely to outperform their peers in key financial metrics.
hbr.org
Iterative Development and Execution
The agile steps explained in iterative development are at the core of successful modern projects. Your development process breaks down into short timeboxed cycles, typically spanning 1-4 weeks, commonly known as sprints. These focused work periods allow your team to build functional portions of products incrementally rather than delivering everything at once.
Cross-functional collaboration drives these agile steps. Your teams combine members with various skills—developers, designers, testers, and business analysts—working closely together. This collaborative approach helps eliminate silos and ensures everyone understands the agile steps explained in your project methodology.
Each sprint delivers working software or tangible features that add immediate value. These agile steps explained through incremental development mean you can:
- Gather user feedback early and often
- Make adjustments based on real usage data
- Reduce risk by testing market fit continuously
- Maintain flexibility to adapt to changing requirements
The incremental nature of agile development methodology allows your team to refine designs throughout the project lifecycle. Instead of finalizing all designs upfront, you evolve them based on lessons learned during each sprint, allowing for continuous improvement of both process and product.
Sprint Execution Framework
Effective sprint execution follows a structured pattern of agile steps explained through daily activities. Each sprint begins with planning sessions where your team selects backlog items to complete. During the sprint, daily stand-up meetings (typically 15 minutes) help everyone stay aligned on progress and obstacles.
Your team maintains a sprint board showing work items in various stages: To Do, In Progress, and Done. This visual management technique makes the agile steps explained in your workflow transparent to all stakeholders and helps project communication flow smoothly.
At the end of each sprint, you conduct two crucial ceremonies: the sprint review (demonstrating completed work to stakeholders) and the retrospective (reflecting on what went well and what could improve). These agile steps explained through regular reflection enable continuous process improvement.
Continuous integration practices support your iterative approach by automatically merging code changes several times daily. This reduces integration problems and validates that your incremental builds remain functional. When implementing these agile steps explained in your technical environment, you’ll need to establish automated testing to maintain quality throughout rapid development cycles.

Continuous Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing isn’t an afterthought in the agile steps explained process—it’s an ongoing activity integrated throughout the development cycle. You’ll find agile approaches emphasize continuous validation rather than leaving quality checks until the end of a project. This ensures issues are caught early when they’re less expensive to fix.
The agile testing approach incorporates several key elements to maintain quality at every step:
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): You’ll write tests before implementing features, ensuring clear understanding of requirements and creating a safety net for future changes.
- Automated Testing: Creating repeatable test scripts saves time and provides consistent results across multiple iterations.
- Continuous Integration: Code changes are regularly merged into a shared repository and automatically tested to detect problems quickly.
- Exploratory Testing: Manual investigation supplements automated tests to find issues that automated processes might miss.
- Pair Programming: Two developers working together catch mistakes in real-time while sharing knowledge.
- Daily Feedback Loops: Regular communication helps identify quality issues before they compound.
Implementing Effective Quality Gates
Quality gates in agile steps explained frameworks serve as checkpoints that prevent defective work from moving forward. You can integrate quality management throughout your development process by implementing these practices:
| Quality Gate | Purpose | Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition of Ready | Ensures user stories are clear before work begins | Sprint planning |
| Code Reviews | Validates code quality and adherence to standards | During development |
| Acceptance Criteria | Verifies features meet requirements | Before task completion |
| Sprint Demo | Validates functionality with stakeholders | End of sprint |
The agile steps explained approach rejects the traditional “test later” mindset in favor of building quality into every step. When issues are discovered, they’re addressed immediately rather than documented for future fixes. This continuous quality focus helps reduce technical debt and prevents the accumulation of defects.
Your testing strategy should evolve alongside your product. As new features are added, test suites must be updated to maintain comprehensive coverage. This adaptability is central to agile explained methodologies and supports the principle of responding to change over following a rigid plan.
By embracing continuous testing, you’ll create a culture where quality is everyone’s responsibility, not just designated testers. This collective ownership of quality helps teams deliver more reliable products with fewer critical defects.
Tools and Technologies for Agile Implementation
Implementing agile steps requires the right toolkit to facilitate your team’s iterative workflows. To support the agile steps explained throughout your project lifecycle, several purpose-built technologies have emerged that enhance collaboration, visibility, and delivery speed.
Selecting appropriate agile tools is crucial for maintaining momentum through each sprint. The most widely adopted project management platforms include:
- Jira: Offers comprehensive agile steps explained through customizable workflows, detailed reporting, and advanced roadmapping capabilities.
- Trello: Provides visual Kanban boards that simplify agile steps explained in card-based workflows.
- Asana: Combines list and board views with timeline features to track agile steps explained across multiple projects.
- Wrike: Features interactive Gantt charts and workload views to balance resources across agile steps explained.
These tools help you enhance project collaboration while automating repetitive tasks to keep your team focused on value delivery.
Essential Features for Agile Success
When evaluating technologies to support your agile steps explained, prioritize these key capabilities:
- Backlog management – Organize user stories and requirements with flexible prioritization.
- Sprint planning – Schedule work iterations with capacity planning.
- Task visualization – Track work progress through customizable boards.
- Automated reporting – Generate burndown charts and velocity metrics.
- Integration capabilities – Connect with version control and continuous integration tools.
Beyond dedicated project management platforms, successful agile implementation relies on complementary technologies. Version control systems like Git help manage code changes across your team, while continuous integration tools automate testing. Communication platforms facilitate the daily standups central to agile steps explained in methodologies like Scrum.
The right tools will help overcome project roadblocks by making your agile steps explained clearly to all stakeholders. They create transparency in decision-making and help track progress throughout each iteration.
By embracing these technologies, you’ll establish a foundation for consistent agile steps explained through standardized processes. This technological support structure enables your team to focus on delivering value rather than managing administrative overhead.
Strategic Benefits and Implementation Insights
Understanding the agile steps explained within your projects can transform how you deliver value to stakeholders. When implemented correctly, agile methodologies offer significant advantages over traditional approaches.
Agile steps explained simply means breaking work into small, manageable iterations with frequent reassessment and adaptation. This approach delivers multiple strategic benefits that directly impact your bottom line.
Key Advantages of Agile Implementation
The agile steps explained in modern project frameworks provide four primary benefits:
- Enhanced Flexibility – You can adapt quickly to changing requirements or market conditions without derailing the entire project. Agile methodologies allow your teams to pivot based on new information, unlike rigid waterfall approaches.
- Accelerated Value Delivery – By releasing functional increments every 1-4 weeks, you provide value to stakeholders faster. Each sprint delivers working features that can be used immediately while development continues.
- Improved Stakeholder Engagement – Regular demos and sprint reviews keep stakeholders involved throughout the project lifecycle. This continuous feedback loop ensures the final product aligns with actual needs. Engaging stakeholders effectively becomes easier with transparent agile processes.
- Higher Product Quality – Continuous testing and integration within the agile steps explained framework catches defects early when they’re less expensive to fix. This results in more reliable products with fewer critical issues at launch.
For optimal implementation, consider these factors when applying agile steps explained in your organization:
- Team Composition – Cross-functional teams with all necessary skills perform better in agile environments.
- Cultural Readiness – Your organization must embrace change, transparency, and continuous improvement.
- Executive Support – Leadership must understand and champion the agile steps explained in your methodology.
- Right-sized Projects – Complex initiatives with uncertain requirements benefit most from agile approaches.
The following table summarizes when to apply agile steps explained in different project scenarios:
| Project Characteristic | Agile Suitability |
|---|---|
| Evolving Requirements | Excellent |
| Stable Requirements | Moderate |
| Innovation-focused | Excellent |
| Fixed Deadline/Budget | Requires discipline |
| Distributed Teams | Challenging but possible |
When implementing agile steps explained methodologies, strong project leadership becomes crucial for navigating the transition from traditional approaches. Your teams will need coaching on agile principles, daily stand-ups, and effective backlog management.
The agile steps explained approach works best when you select the right tools for your specific needs. Consider your team size, project complexity, and integration requirements when choosing between platforms like Jira, Trello, or Asana.
Practical Application and Future Outlook
Transitioning to Agile requires a thoughtful approach rather than an overnight switch. You’ll need to follow these agile steps explained carefully to ensure success. Start by implementing Agile in a small pilot project before expanding across your organization. This allows your team to learn the fundamentals while minimizing disruption.
Creating a hybrid approach often works best when transitioning from traditional methods. You can integrate flexible delivery frameworks that combine Waterfall planning with Agile execution to ease the transition.
Implementation Best Practices
When applying the agile steps explained in real-world scenarios, follow these critical practices:
- Invest in proper training for all team members on agile steps explained
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities within the Agile framework
- Create dedicated physical or virtual spaces for collaboration
- Develop transparent communication channels for continuous feedback
- Start with basic Agile practices before adding complexity
- Focus on delivering value in each iteration
Remember that agile steps explained aren’t just processes but represent a mindset shift. Your organization will need to embrace values of transparency, adaptability, and customer-centricity to truly benefit from Agile.
Common implementation challenges include resistance to change, misalignment between agile steps explained and organizational culture, and difficulty maintaining focus on continuous improvement. Mitigate these by involving leadership early, celebrating small wins, and practicing active listening to address concerns.
Looking ahead, Agile methodologies will continue evolving with emerging technologies. The future of iterative project management includes increased automation of repetitive tasks, AI-assisted planning and estimation, and improved remote collaboration tools. Distributed teams will utilize enhanced virtual workspaces that replicate in-person collaboration experiences.
The following table summarizes how agile steps explained will evolve in the near future:
| Current Agile Approach | Future Evolution |
|---|---|
| Manual sprint planning | AI-assisted planning and estimation |
| Basic remote collaboration | Immersive virtual team workspaces |
| Manual testing processes | Automated continuous testing |
| Team-level agility | Organization-wide agility |
| Basic metrics tracking | Predictive analytics for project outcomes |
By understanding these agile steps explained and preparing for future trends, you’ll position your projects for success in an increasingly dynamic business environment where continuous improvement is essential for maintaining competitive advantage.