Managing Agile Software Development
Managing agile software development combines structure and flexibility to help teams deliver quality software efficiently. Effective agile management gives your organization the tools to adapt to changing requirements while maintaining productivity and meeting market demands.
Why Managing Agile Software Development Is Critical for Business Success
Effective agile software development management provides businesses a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced digital environment. Well-implemented agile practices cut time-to-market, boost product quality, and enhance customer satisfaction through quick iterations based on feedback. Organizations that excel at agile project management can quickly adjust to market shifts, optimize resources, and build a culture of continuous improvement that fuels innovation. This approach helps you balance stability with adaptability, creating sustainable development processes that deliver consistent value while adjusting to shifting business priorities.
Agile methodologies allow your development teams to break projects into smaller, manageable segments. This division makes tracking progress easier and enables faster problem resolution. Your teams can deliver working software regularly, giving stakeholders frequent opportunities to evaluate and provide input.
The transparency built into agile management frameworks improves communication between team members, stakeholders, and clients. Daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives create feedback loops that keep everyone aligned on project goals and challenges.
Software development teams working under agile management often show higher engagement and motivation. The autonomy granted to self-organizing teams empowers developers to take ownership of their work and contribute meaningfully to project success.
Managing Agile Software Development: Essential Best Practices
Effective agile software development management blends flexibility with structure to drive exceptional results. You’ll find that implementing proven agile practices transforms how your teams collaborate and deliver value to customers. The agile methodology prioritizes adaptability through iterative cycles, allowing for quick pivots based on feedback and changing requirements.
Success in managing agile software development starts with setting clear sprint objectives and conducting focused daily stand-ups. Your team’s productivity will increase when you maintain disciplined backlog management that prioritizes high-value features. This approach ensures everyone understands what needs to be built and why it matters.
Cross-functional teamwork eliminates traditional departmental barriers that can slow innovation. By building strong cross-functional teams, you create environments where diverse skills combine to solve complex problems efficiently.
Regular retrospectives provide opportunities to refine processes continuously. Your commitment to these improvement sessions demonstrates that managing agile software development isn’t static but evolves with each iteration.
1. Establish Clear and Concise Sprint Goals
Successfully managing agile software development begins with defining specific, measurable objectives for each sprint. When you establish clear goals, team members understand exactly what they’re working toward and can better prioritize their efforts. Ensure these goals align with the overall product vision to maintain strategic direction throughout the development process.
Communicate objectives effectively to all stakeholders, including developers, product owners, and business representatives. This transparency helps prevent misunderstandings and keeps everyone focused on the same outcomes. Using SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) provides a structured framework for effective goal-setting that enhances your agile implementation.
Consider creating a shared document that outlines sprint goals and making it accessible to the entire team. This visual reminder helps maintain focus and alignment throughout the sprint cycle.
2. Implement Daily Stand-up Meetings
Effective daily stand-ups are crucial when managing agile software development teams. These brief synchronization meetings should never exceed 15 minutes, focusing exclusively on three key questions: what was accomplished yesterday, what will be done today, and what obstacles stand in the way.
By maintaining a consistent schedule and format for these meetings, you create a predictable rhythm that teams can rely on. Choose a fixed time—preferably in the morning—and a designated location or virtual meeting space. This consistency helps team members prepare their updates efficiently.
Equal participation from all team members is essential for productive stand-ups. Encourage everyone to contribute concisely while avoiding detailed technical discussions that can derail the meeting. These discussions should be noted and handled separately with only relevant team members.
Standing during the meeting (as the name suggests) naturally keeps things brief and energized. You can further enhance team collaboration by rotating the meeting facilitator role, giving each team member an opportunity to develop leadership skills while maintaining the meeting’s focus and pace.
Expert Insight: To optimize daily stand-up meetings, keep them under 15 minutes and focused on three questions: yesterday’s accomplishments, today’s goals, and obstacles. Ensure equal participation and avoid deep technical discussions. Encourage brevity by having everyone stand and rotate the facilitator role to foster leadership skills within the team.
3. Prioritize Backlog Management
Effective backlog management is the heartbeat of managing agile software development success. You need to establish a rhythm of regular backlog refinement sessions where items are reviewed, updated, and reprioritized based on changing business needs and technical discoveries.
When managing your agile backlog, implement structured prioritization frameworks like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) to ensure the highest-value items rise to the top. These techniques provide objective criteria for decision-making when stakeholders disagree about priorities.
Product owners must actively participate in grooming sessions to:
- Clarify requirements and acceptance criteria
- Answer developer questions about functionality
- Represent customer needs and business value
- Help break down complex user stories
Breaking larger epics into smaller, manageable user stories helps prevent scope creep and enables more accurate estimation. Your development team will appreciate having properly sized tasks that can be completed within a single sprint cycle. Effective project collaboration during backlog refinement ensures everyone understands both the what and the why behind prioritized items.
Expert Insight: Prioritize backlog management by holding regular refinement sessions to ensure items are updated and aligned with business needs. Utilize structured frameworks like MoSCoW or WSJF for objective prioritization, and involve product owners to clarify requirements and enhance team understanding. This approach fosters effective collaboration and prevents scope creep.
4. Foster Cross-functional Collaboration in Agile Development
Effective cross-functional teamwork is essential when managing agile software development projects. Breaking down organizational silos between development, testing, and operations teams creates an environment where innovation can flourish. You’ll notice increased productivity when team members freely share knowledge and skills across traditional role boundaries.
Create dedicated collaboration spaces, whether physical or virtual, where team members can easily interact. These environments should facilitate spontaneous discussions and problem-solving sessions that spark creative solutions. Tools like digital whiteboards and project collaboration platforms help remote teams maintain strong connections despite geographical distance.
Implement practices that promote shared responsibility, such as:
- Pair programming sessions where developers work together on code
- Cross-functional code reviews involving different team specialties
- Shared ownership of quality through test-driven development
- Collective estimation and planning activities
Encourage team members to develop T-shaped skills—deep expertise in their specialty combined with broader knowledge across disciplines. This versatility allows for more flexible resource allocation and better cross-functional product development when managing agile software development initiatives.
Expert Insight: Foster cross-functional collaboration in agile development by creating dedicated spaces for interaction and using digital tools for remote teams. Encourage practices like pair programming and cross-functional code reviews to promote shared responsibility. Developing T-shaped skills enhances versatility, leading to more effective resource allocation and innovative solutions.
5. Embrace Continuous Improvement Through Retrospectives
Successful managing agile software development requires a commitment to ongoing refinement of your processes. Schedule retrospective meetings at the conclusion of each sprint to evaluate what worked well and what needs improvement. These sessions should create a psychologically safe space where team members feel comfortable providing honest feedback without fear of blame or criticism.
When facilitating retrospectives, focus on identifying actionable improvements rather than dwelling on past mistakes. A productive approach is to use frameworks like “Start, Stop, Continue” or “What went well, what didn’t, what can we improve?” to structure the conversation. These formats help your team prioritize the most impactful changes to implement in the next sprint.
To maximize the value of retrospectives, consider these key elements:
- Preparation: Send agenda items beforehand so team members can reflect
- Documentation: Record agreed action items and assign owners
- Time-boxing: Keep sessions focused (typically 1-2 hours)
- Follow-up: Begin the next retrospective by reviewing previous action items
The true value of retrospectives comes from implementing the continuous improvement ideas they generate. Track each action item’s progress between sprints to ensure accountability and demonstrate the tangible benefits of the retrospective process to your team.
Expert Insight: To foster continuous improvement in agile software development, hold structured retrospectives at the end of each sprint. Focus on actionable insights using frameworks like “Start, Stop, Continue,” and ensure follow-up on action items to promote accountability. This empowers your team to enhance processes and drive meaningful change.
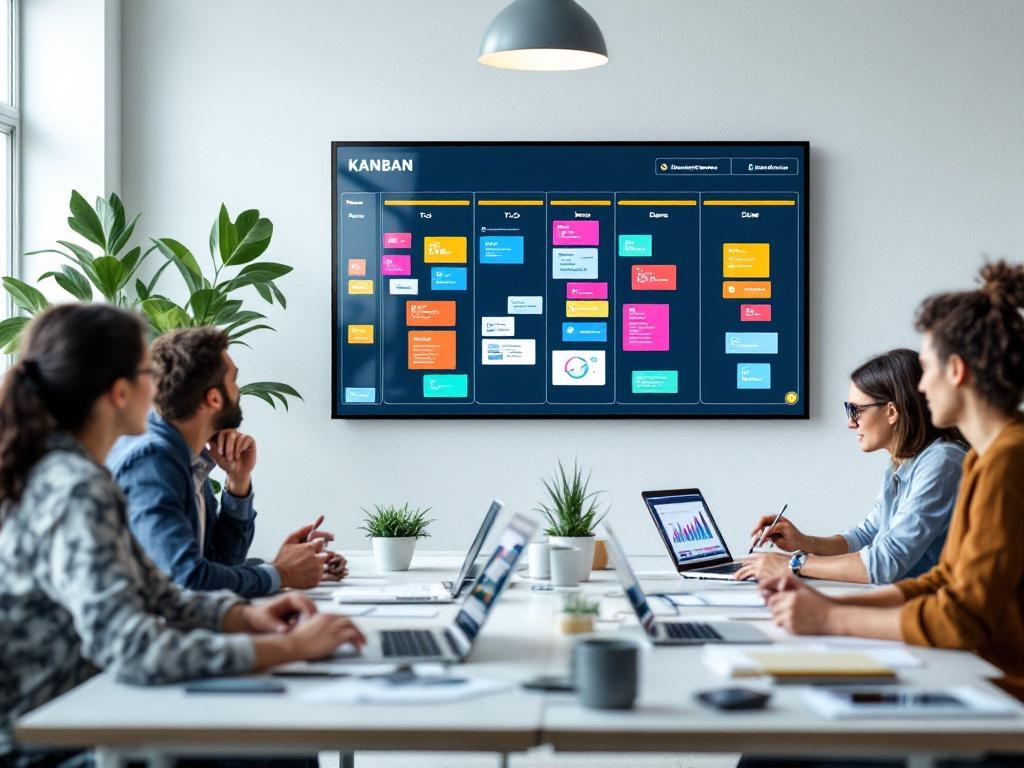
6. Maintain Visible Progress Tracking for Managing Agile Software Development
Effective progress tracking stands as a cornerstone when managing agile software development teams. Visual management tools provide immediate transparency into your project status and workflow bottlenecks.
Implement digital or physical Kanban boards that display work items transitioning through various stages from “to-do” to “done.” These boards create a shared understanding of current work distribution and highlight potential workflow issues before they escalate. Kanban boards for project management enable teams to self-organize around visible work.
Update burndown and burnup charts after each daily stand-up meeting to track sprint progress against commitments. These visual indicators help forecast completion dates and identify when adjustments might be necessary.
Consider implementing these visibility practices:
- Position information radiators in high-traffic areas where team members frequently pass
- Use color-coding to highlight blocked items or urgent priorities
- Make dashboards accessible to stakeholders outside the immediate team
- Standardize metrics across projects for organizational consistency
- Conduct brief weekly “tour of the boards” sessions to ensure everyone understands status
Remember that visual management works best when combined with strong project collaboration practices and regular discussion of what the metrics reveal about your development process.

7. Adapt to Change Through Short Feedback Loops
Successfully managing agile software development requires creating systems that embrace change rather than resist it. Short feedback loops are essential for maintaining your project’s relevance and value in evolving markets. You should establish regular checkpoints with customers to gather insights about your product’s performance and areas for improvement.
When market conditions shift, be prepared to adjust your priorities accordingly. This doesn’t mean abandoning your sprint commitments mid-cycle, but rather incorporating continuous improvement into your planning process. Each new sprint presents an opportunity to realign with changing business needs.
Integrate user testing throughout your development cycles instead of waiting until the end. Consider these approaches to implement effective feedback loops:
- Conduct weekly user interviews with key stakeholders or customer representatives
- Deploy feature toggles to test new functionality with limited user groups
- Use A/B testing for data-driven decision making
- Schedule regular demos with stakeholders beyond the formal sprint reviews
While maintaining flexibility, you must still protect sprint integrity. Agile methodology works best when teams can focus without constant disruption. The goal is to be responsive without becoming reactive to every change request.

Managing agile software development combines structured methodologies with adaptable frameworks to deliver high-quality products efficiently. This approach emphasizes clear sprint goals, daily stand-ups, backlog management, cross-functional collaboration, continuous improvement through retrospectives, visible progress tracking, and adaptable feedback loops to navigate the complex landscape of modern software development.
Managing agile software development has become essential for enterprise environments facing increased market competition and rapidly evolving technology landscapes. This methodology enables organizations to respond quickly to changing requirements, reduce time-to-market, enhance product quality through iterative development, and improve team morale by fostering autonomy and purpose-driven work—ultimately delivering greater business value while maintaining the flexibility needed in today’s dynamic business environment.
Key Agile Management Insights
Successfully managing agile software development requires a comprehensive approach that balances structure with flexibility. The seven best practices outlined in the article provide a framework for implementing effective agile methodologies that drive productivity and quality outcomes. Clear sprint goals and daily stand-ups create alignment and communication efficiency, while prioritized backlog management ensures teams work on high-value items first. Cross-functional collaboration breaks down silos, continuous improvement through retrospectives refines processes, and visible progress tracking maintains transparency. Finally, short feedback loops enable teams to adapt quickly while protecting sprint integrity.
Essential Implementation Steps
- Establish SMART sprint goals aligned with product vision and share them in a team-accessible document.
- Schedule consistent 15-minute daily stand-ups focusing on accomplishments, plans, and obstacles.
- Implement regular backlog refinement sessions using frameworks like MoSCoW to prioritize work.
- Create dedicated collaboration spaces for cross-functional teams and implement pair programming.
- Conduct structured retrospectives using frameworks like “Start, Stop, Continue” with clear action items.
- Deploy visual management tools like Kanban boards and burndown charts for transparent progress tracking.
- Establish regular customer feedback checkpoints and integrate continuous user testing throughout development.
- Rotate meeting facilitation roles to develop leadership skills across the team.
- Break complex work into smaller user stories to improve estimation accuracy and prevent scope creep.
- Balance flexibility with focus by protecting sprint integrity while remaining responsive to change.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What makes sprint goals effective in agile software development?
Effective sprint goals are specific, measurable, aligned with product vision, and communicated clearly to all stakeholders. They provide focus for team members and help them prioritize their efforts within the sprint timeframe.
- How can I make daily stand-up meetings more productive?
Keep meetings under 15 minutes, focus strictly on three questions (yesterday’s work, today’s plan, and obstacles), ensure equal participation, avoid technical discussions, and consider rotating the facilitator role to develop leadership skills across the team.
- What prioritization frameworks work best for backlog management?
Structured frameworks like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) and Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) provide objective criteria for decision-making when stakeholders disagree about priorities.
- How do retrospectives contribute to agile team improvement?
Retrospectives create a safe space for honest feedback, focus on actionable improvements rather than past mistakes, and employ frameworks like “Start, Stop, Continue” to structure conversations. Tracking action items between sprints ensures accountability and demonstrates value.
- What visual tools are most effective for tracking agile progress?
Kanban boards show work transitioning through various stages, while burndown and burnup charts track sprint progress against commitments. Color-coding can highlight blocked items, and standardized metrics provide organizational consistency.
- How can agile teams balance adaptability with sprint integrity?
Create systems that embrace change through short feedback loops and regular customer checkpoints, while protecting teams from constant disruption. Adjust priorities between sprints rather than mid-cycle to maintain focus while remaining responsive to evolving needs.