The Six Sigma Methodology
The Six Sigma methodology emerged in 1986 as a groundbreaking data-driven approach to quality management, created by Bill Smith at Motorola. This framework strives for near-perfection in business processes by cutting defects to just 3.4 per million opportunities, delivering a 99.9997% defect-free output across manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and supply chain operations.
Key Takeaways
- Six Sigma focuses on systematic process improvement through rigorous statistical analysis and measurement.
- The methodology targets near-zero defects, with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
- Applicable across diverse industries, from manufacturing to healthcare and financial services.
- Drives continuous improvement through data-driven decision-making.
- Helps organizations reduce process cycle times and increase operational efficiency.
Organizations implement Six Sigma principles to eliminate variations in their processes. You’ll find this approach particularly effective for standardizing operations and reducing waste. The methodology uses statistical tools to identify root causes of problems rather than just treating symptoms.
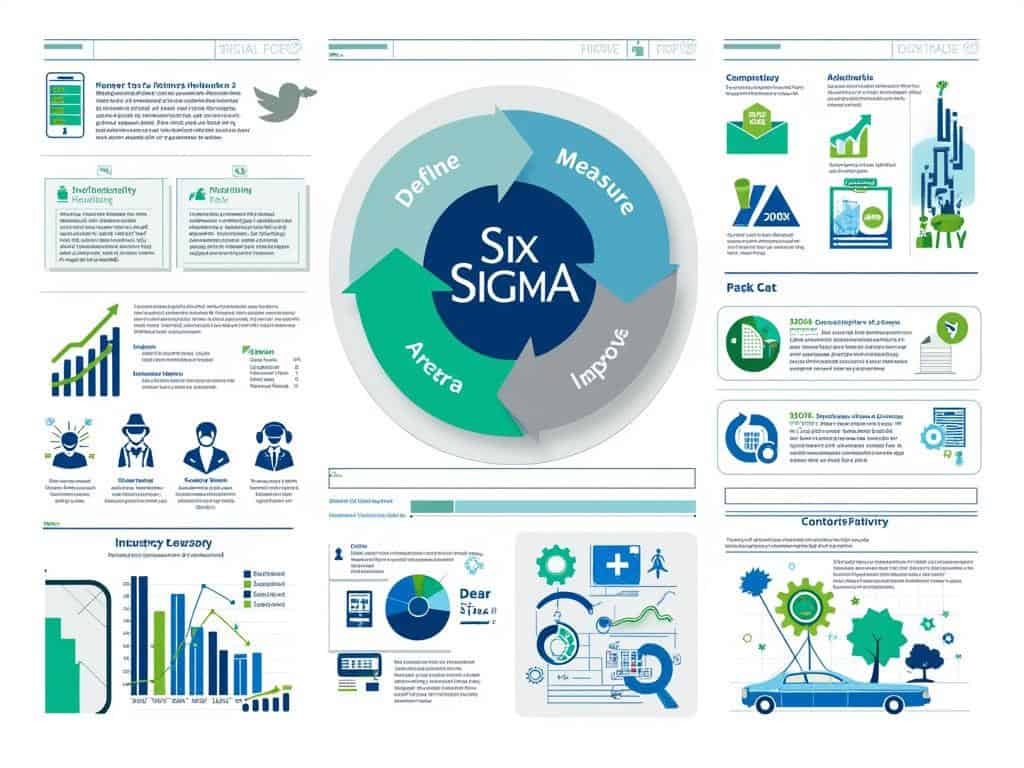
Companies that adopt Six Sigma often experience substantial cost savings alongside quality improvements. Your team can benefit from the structured DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) that guides improvement projects from start to finish.
Training plays a critical role in Six Sigma implementation, with practitioners earning certifications ranging from Yellow Belt to Master Black Belt. Each certification level indicates different expertise depths and project leadership capabilities within the Six Sigma framework.
Top companies including General Electric, Bank of America, and Amazon have successfully integrated this methodology into their business strategies. Your organization can achieve similar results by focusing on customer requirements and developing clear metrics for success.
The complementary relationship between Six Sigma and other improvement methodologies like Lean manufacturing has created hybrid approaches that address both waste reduction and quality enhancement simultaneously.
“Embracing the 6 Sigma methodology transforms organizations into bastions of operational excellence, where data-driven precision reduces defects to an astonishing 3.4 per million opportunities. This relentless pursuit of near-perfection not only enhances quality but propels continuous improvement across diverse industries, unlocking unparalleled efficiency and success.”
Origins and Fundamental Concept
The 6 sigmas methodology emerged in 1986 when Bill Smith at Motorola developed this revolutionary approach to quality management. At its core, 6 sigmas aims to achieve near-perfection in business processes by reducing defects to just 3.4 per million opportunities (DPMO), representing an impressive 99.9997% defect-free output. This data-driven approach has transformed how organizations tackle quality challenges across manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and supply chain sectors.
The Universal Application of 6 Sigmas
You’ll find 6 sigmas applicable to virtually any business process regardless of industry. This methodology focuses on transforming operations through statistical analysis and measurement rather than relying on gut feelings or assumptions. When you implement a Six Sigma black belt project, you’ll address process variation systematically, eliminating the root causes of defects.
The beauty of 6 sigmas lies in its versatility. You can apply its principles to:
- Manufacturing processes to reduce product defects
- Healthcare systems to minimize medical errors
- Financial operations to decrease transaction mistakes
- Supply chain management to optimize delivery accuracy
- Customer service to enhance satisfaction metrics
The methodology doesn’t simply fix problems—it fundamentally changes how you approach process management. By establishing clear metrics and focusing on variance reduction, 6 sigmas provides a framework for continuous improvement that yields measurable results.
What distinguishes 6 sigmas from other quality improvement approaches is its relentless focus on data. Every process improvement decision stems from statistical analysis rather than intuition. This approach requires you to collect detailed measurements, analyze variation patterns, and implement solutions based on factual evidence.
Organizations that successfully implement 6 sigmas typically experience:
- 25-70% reduction in process cycle times
- 12-18% increase in capacity utilization
- Significant cost savings through defect reduction
- Enhanced customer loyalty through improved quality
When using commonly applied six sigma metrics, you’ll track progress through sigma level measurements, which quantify how your processes perform relative to customer requirements. This statistical foundation provides clear visibility into improvement opportunities and helps prioritize initiatives that deliver maximum business impact.
The transformative power of 6 sigmas comes from its systematic approach to process excellence, combining rigorous data analysis with practical improvement methods to drive meaningful organizational change.
Expert Insight: To harness the full potential of the 6 Sigmas methodology, focus on embedding a data-driven culture within your organization, where every decision is supported by statistical analysis. By systematically identifying and addressing process variations, you can not only eliminate defects but also establish continuous improvement as a key organizational value. Remember, the foundation of 6 Sigmas lies in leveraging clear metrics to drive insights and prioritize initiatives that yield the greatest impact on quality and operational efficiency.
Core Principles of Six Sigma
Six Sigma serves as a powerful data-driven methodology that helps you transform your business processes through systematic improvement. Developed by Bill Smith at Motorola in 1986, 6 sigmas represents an approach that aims to reduce defects to just 3.4 per million opportunities – an impressive 99.9997% defect-free performance.
The foundation of 6 sigmas rests on several key principles that drive its effectiveness across industries from manufacturing to healthcare. Your implementation of these principles can significantly enhance operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Essential Six Sigma Principles
You’ll find these core elements at the heart of every successful 6 sigmas implementation:
- Customer-centric focus – Every process improvement begins with understanding what creates value for your customers
- Data-driven decision making – Relying on facts rather than assumptions to guide improvement efforts
- Process variation reduction – Consistently working to minimize deviations in outputs
- Structured problem-solving – Following the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology
- Leadership commitment – Ensuring top-level support for quality initiatives
- Cross-functional collaboration – Breaking down silos to leverage diverse expertise
The DMAIC framework provides a structured approach for your process improvement system. This methodical cycle helps you tackle complex problems systematically, ensuring that 6 sigmas isn’t just a one-time fix but a continuous journey toward excellence.
When implementing 6 sigmas, you’ll need to establish clear metrics. This table outlines the common performance levels in Six Sigma:
| Sigma Level | Defects Per Million | Process Yield |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 308,537 | 69.2% |
| 3 | 66,807 | 93.3% |
| 4 | 6,210 | 99.4% |
| 5 | 233 | 99.98% |
| 6 | 3.4 | 99.9997% |
The pursuit of 6 sigmas excellence requires both statistical tools and leadership skills. You’ll need to combine analytical techniques like control charts and Pareto analysis with effective project leadership to drive meaningful change.
Many organizations integrate Lean principles with Six Sigma, creating a powerful approach that eliminates waste while reducing variation. This combined methodology helps you achieve faster process cycles with fewer defects, ultimately delivering superior value to customers.
By embracing these 6 sigmas principles, you’ll create a culture of continuous improvement where data drives decisions and customer satisfaction remains the ultimate measure of success. The methodology provides a clear path to operational excellence through disciplined analysis and systematic process enhancement.
Companies that adopt Six Sigma see a reduction in defects of up to 50% and an average return on investment of nearly $5 for every $1 spent.
forbes.com
DMAIC Methodology: The Six Sigma Framework
The DMAIC methodology forms the backbone of 6 sigma implementation, providing a structured approach to tackle complex business challenges. This data-driven framework helps you systematically improve processes while eliminating defects and reducing variation. Each phase of DMAIC builds upon the previous one, creating a powerful cycle of continuous improvement.
The Define phase establishes clear project goals and identifies critical customer requirements. You’ll document the problem statement, establish project scope, and set measurable objectives. This crucial first step ensures everyone understands what constitutes success and how it aligns with customer needs. At this stage, you’ll develop a project charter and identify key stakeholders to enhance stakeholder satisfaction throughout the project.
In the Measure phase, you’ll gather baseline performance data to quantify the current state of your process. This involves collecting relevant metrics, validating measurement systems, and establishing process capability. By understanding your current performance level, you can set realistic improvement targets. The 6 sigma approach emphasizes data integrity – you can’t improve what you can’t accurately measure.
The Analyze phase uses statistical tools to identify root causes of problems and process inefficiencies. You’ll examine relationships between variables and determine which factors most significantly impact performance. This evidence-based approach prevents you from making assumptions about what’s causing issues in your process. Proper analysis helps you conduct a root cause analysis that targets true problems rather than symptoms.
During the Improve phase, you’ll develop and implement solutions to address the identified root causes. This involves brainstorming potential improvements, selecting the most promising options, and testing them through pilots. The 6 sigma methodology ensures changes are driven by data, not hunches or opinions. You’ll optimize solutions through experimentation and validate results with statistical analysis.
The Control phase establishes mechanisms to sustain improvements over time. You’ll implement process controls, document procedures, and create monitoring systems to prevent backsliding. This crucial final step often separates successful 6 sigma projects from failed initiatives. Without proper control measures, processes tend to drift back toward previous performance levels.
Statistical tools and techniques form the foundation of the 6 sigma approach throughout the DMAIC cycle. These include control charts, process capability analysis, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis. These powerful methods allow you to make data-driven decisions with confidence rather than relying on intuition.
Key Benefits of DMAIC Implementation
The structured DMAIC methodology delivers several advantages to your organization:
- Provides a systematic approach to problem-solving
- Establishes clear metrics for success
- Creates sustainable process improvements
- Reduces defects and process variation
- Increases customer satisfaction
- Delivers measurable financial returns
- Builds analytical capabilities across teams
When properly implemented, the 6 sigma DMAIC framework transforms how you approach business challenges, creating a culture of continuous improvement powered by data-driven excellence.

Essential Six Sigma Tools and Techniques
Your success with Six Sigma implementation depends heavily on mastering key analytical tools that drive process improvement. These tools transform raw data into actionable insights, helping you identify and eliminate the root causes of defects.
Cause and Effect (Fishbone) Analysis serves as a powerful visual tool in Six Sigma methodologies. This diagram helps you trace defects back to their potential causes across categories like people, processes, equipment, and materials. When conducting a root cause analysis, this technique provides a structured approach to brainstorming all possible factors contributing to process issues.
Process mapping creates detailed visual representations of workflows, highlighting bottlenecks and inefficiencies. This fundamental Six Sigma tool gives you clarity on how work actually moves through your organization. By creating a comprehensive process map in project management, you gain visibility into areas needing improvement before implementing changes.
Statistical tools form the backbone of data analysis in Six Sigma projects:
- Pareto Charts: Identify the vital few factors causing most problems (80/20 rule)
- Control Charts: Monitor process stability and detect variations
- Histograms: Visualize data distribution and variation patterns
- Scatter Plots: Examine relationships between variables
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis): Anticipate potential failures proactively
The DMAIC project framework structures these tools into a cohesive methodology. Each Six Sigma project progresses through Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control phases, with specific tools deployed at each stage to drive data-driven decisions.
Integrating Tools for Maximum Impact
Successful Six Sigma implementations require combining multiple tools strategically. For example, you might first use process mapping to understand workflows, then apply Pareto analysis to identify critical issues, followed by statistical analysis to validate root causes, and finally implement control charts to sustain improvements.
The power of Six Sigma lies in this systematic approach to problem-solving. Unlike ad-hoc improvement efforts, Six Sigma provides a disciplined methodology backed by statistical rigor. Bill Smith at Motorola developed this approach in 1986, aiming for near-perfect quality with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
When implementing these tools, focus on aligning them with your project success criteria. The tools should support your specific business objectives rather than becoming box-ticking exercises. This practical application distinguishes truly effective Six Sigma practitioners from those who merely understand the theory.

Lean Six Sigma: Integrated Process Improvement
Lean Six Sigma merges two powerful methodologies to create a comprehensive approach to business excellence. You’ll find this integrated framework combines Lean’s focus on eliminating waste with Six Sigma’s emphasis on reducing variation—creating a potent system for organizations seeking operational excellence.
The core strength of Six Sigma lies in its data-driven approach to problem-solving. This methodology targets a near-perfect 99.9997% defect-free output, allowing only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. When implemented properly, you’ll achieve remarkable improvements in quality, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction.
Key Components of Integrated Improvement
The integration of Lean and Six Sigma creates a powerful toolkit for process optimization. Here are the essential elements that make this approach so effective:
- Value Stream Mapping to identify waste and value-adding activities
- 5S workplace organization principles for optimal efficiency
- Statistical analysis techniques to measure process capability
- Cross-functional teams to drive comprehensive improvements
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology for structured problem-solving
- Visual management tools to maintain process control
Organizations implementing Lean Six Sigma can expect significant benefits across multiple dimensions. This comprehensive Six Sigma approach delivers measurable results by targeting both waste and variation simultaneously.
When implementing Lean Six Sigma, you’ll progress through certification levels from Yellow Belt to Green Belt to Black Belt. Each level represents increasing mastery of the tools and techniques required to drive process improvement. Master Black Belts serve as organization-wide mentors and trainers, ensuring the methodology becomes embedded in your culture.
The practical implementation of Six Sigma relies on robust statistical tools like control charts, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis. These tools help you identify the root causes of problems rather than just addressing symptoms. By focusing on commonly used Six Sigma metrics, your organization can quantify improvements and justify investments in process changes.
Successful Lean Six Sigma projects typically follow a structured approach. You’ll first identify critical business issues, then assemble cross-functional teams to address them using the DMAIC methodology. The rigorous data collection and analysis inherent in Six Sigma ensures that decisions are based on facts rather than assumptions or opinions.
Practical Implementation and Benefits
Implementing 6 sigmas in your organization requires a structured approach and proper resource allocation. Your journey toward operational excellence begins with understanding the certification levels and establishing the right teams for successful implementation.
Certification Hierarchy and Team Structure
The 6 sigmas methodology uses a belt-based certification system that defines roles and responsibilities within your improvement projects:
- White Belt: Entry-level practitioners with basic understanding of 6 sigmas concepts
- Yellow Belt: Team members who support specific improvement projects
- Green Belt: Project leaders who manage smaller projects while maintaining regular job duties
- Black Belt: Full-time project leaders handling complex improvements and mentoring others
- Master Black Belt: Organization-wide experts who train others and oversee strategic initiatives
Creating cross-functional teams for your 6 sigmas projects is essential. These teams should include members from different departments who can provide diverse perspectives and expertise. This collaborative approach to 6 sigmas projects ensures comprehensive problem-solving and better adoption of solutions.
The tangible benefits of implementing 6 sigmas span across industries and functions:
- Quality improvements through reduced defects and process variations
- Significant cost reductions via elimination of waste and rework
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through consistent product/service delivery
- Increased operational efficiency with streamlined processes
- Improved employee engagement and problem-solving capabilities
Organizations that have successfully implemented 6 sigmas report substantial financial gains. Motorola, the birthplace of 6 sigmas, documented $17 billion in savings over its first decade of implementation. General Electric reported over $10 billion in savings during its first five years of adoption.
Your 6 sigmas implementation journey requires leadership commitment and a cultural shift toward data-driven decision-making. Successful organizations view 6 sigmas not as a short-term project but as a fundamental continuous improvement philosophy embedded in everyday operations.
When implementing 6 sigmas, you’ll need to:
- Identify strategic business opportunities with measurable impact
- Select and train appropriate team members
- Execute projects using the DMAIC methodology
- Track and communicate results
- Standardize successful changes across the organization
This systematic approach ensures your 6 sigmas initiatives deliver consistent results and build momentum for future improvements.